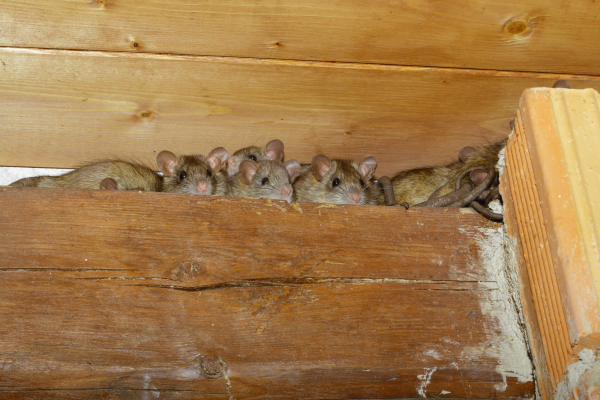
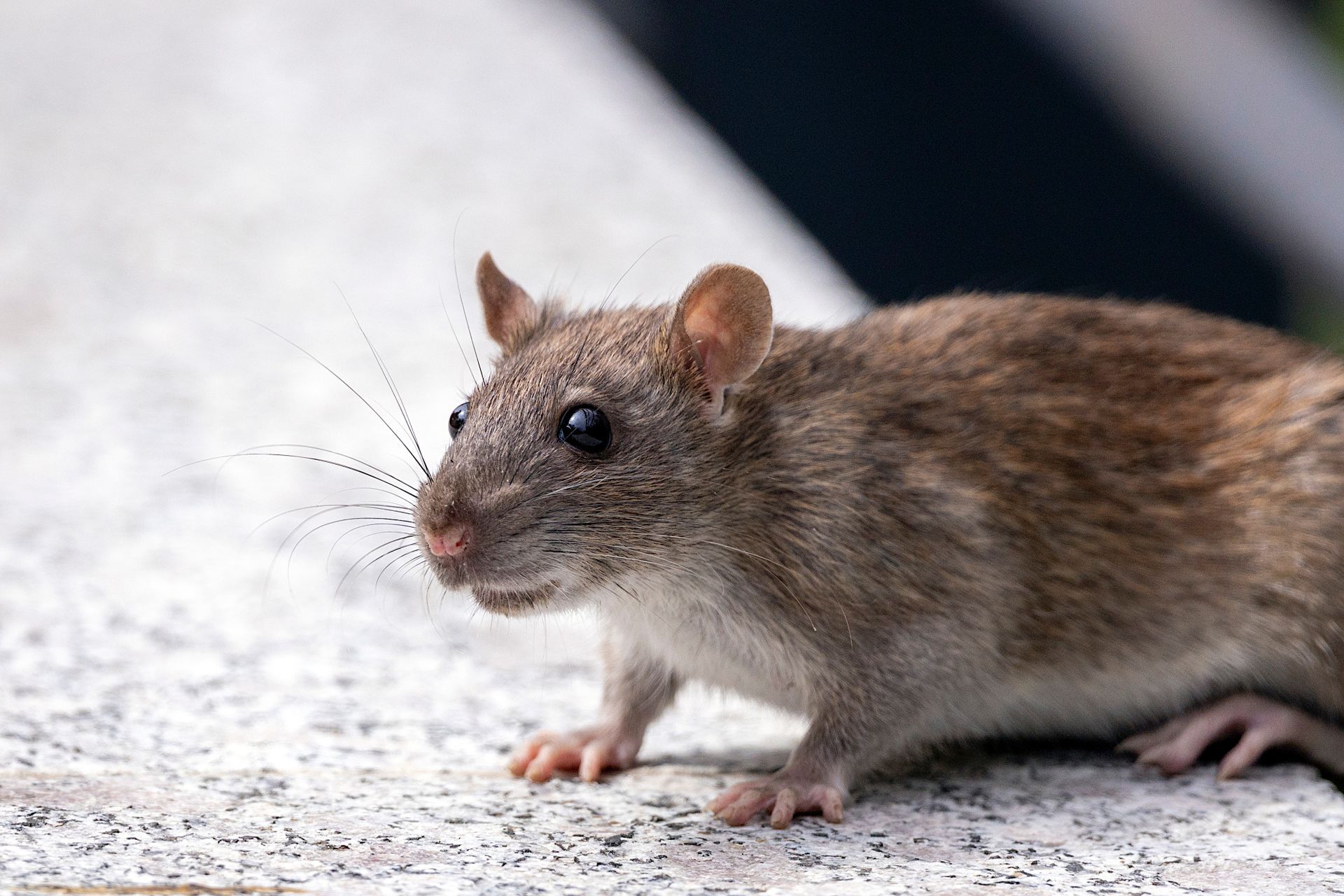
Rats And Mice
Rats and mice are rodents which mean their teeth continually grow, so they have to gnaw on wood or similar items to wear their teeth down. Rats will chew anything and they like to sleep near warm spots, and they often chew light fittings and electrical cables. They also bite plastic including plastic water-pipes and flexible water hoses on dishwashers. They often make holes in walls and build nests in insulation. This is why we recommend starting a rodent removal program immediately.
The Rodent Pros Offer rodent trapping, rodent removal, rodent exclusion, rodent sanitation and rodent remediation services to all cities within a 50 miles radius of Tampa Florida.
Identifying A Rodent Infestation
If you're dealing with a rodent infestation and are within 50 miles of Tampa Florida The Rodent Pros are here to help.
-Identify the rodent infestation Look for signs of rat activity, such as droppings, gnaw marks, chewed wires, and shredded materials. This will help you confirm a rodent infestation and determine the extent.
-Remove food sources Rats are attracted to easily accessible food. Securely store food in sealed containers, clean up any spills or crumbs, and ensure outdoor garbage bins are tightly sealed. By removing their food source, you can make your property less likely to experience a rat infestation.
-Seal entry points Inspect your home or building for any gaps, cracks, or openings that rats could use to enter. Pay close attention to areas around pipes, vents, doors, and windows. Seal these openings with durable materials like steel wool or caulk to prevent a rat infestation.
-Trim vegetation Rats often use overgrown vegetation as hiding spots or pathways. Trim tree branches, shrubs, and tall grass near your property to eliminate potential hiding places and make it harder for rats to approach your home.
-Consult a professional If the infestation is severe or you're having difficulty controlling the rat population on your own, The Rodent Pros has the experience, and tools to effectively deal with rat infestations.
-Maintain cleanliness Regularly clean and declutter your property, both indoors and outdoors. This reduces potential hiding spots for rats and makes it easier to identify any new signs of a rodent infestation.
Remember, it's important to address a rat infestation promptly as rats can carry diseases and cause damage to your property. Taking preventive measures and seeking professional help when necessary will help you tackle the issue effectively.
Importance of Species Identification
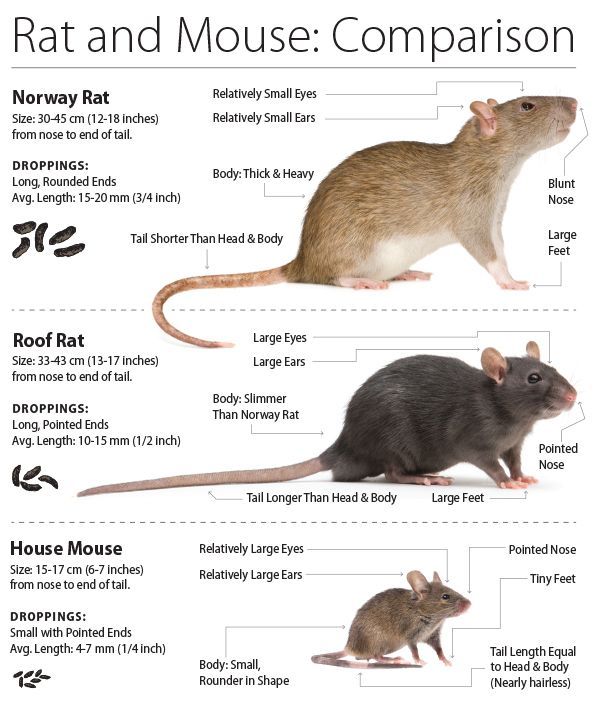
Norway Rat (Rattus norvegicus) Also known as the brown rat or sewer rat, the Norway rat is one of the most common rat species found in urban areas. They have brown or gray fur, a stocky body, and a blunt snout. Norway rats are excellent climbers and diggers, and they often establish their nests in burrows near food sources.
Roof Rat (Rattus rattus) Roof rats, also called black rats or ship rats, are another common rat species in Tampa. They have sleek bodies, long tails, and large ears. Roof rats are skilled climbers and are often found nesting in attics, trees, and elevated areas. They prefer fruits, vegetables, and grains as their primary food sources.
House Mouse (Mus musculus) House mice are small rodents with a slender body, large ears, and a long tail. They are adaptable and can be found in both urban and rural environments. House mice tend to nest in walls, cabinets, and other hidden areas, and they have a diet that includes grains, seeds, and various food scraps.
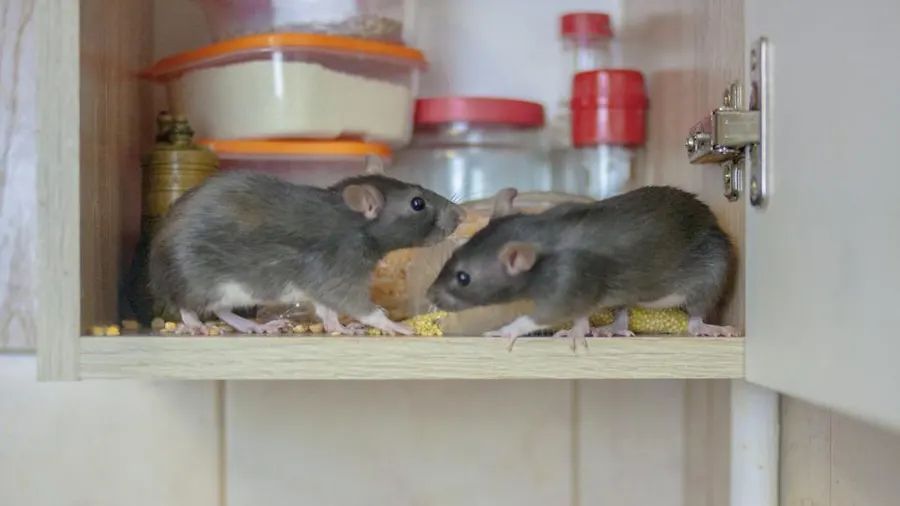

The breeding cycle of rats can vary depending on the species, environmental conditions, and availability of resources. Here is a general overview of the rat breeding cycle
Sexual maturity Rats reach sexual maturity relatively quickly. Female rats typically reach sexual maturity around 5 to 6 weeks of age, while male rats may mature slightly later, at around 8 to 10 weeks of age.
Estrous cycle Female rats have a regular estrous cycle, which refers to the period of receptivity to mating. The estrous cycle of rats is relatively short, typically lasting 4 to 5 days. If mating occurs during this period, the female rat can become pregnant.
Gestation period The gestation period, or the time from conception to birth, for rats is typically around 21 to 23 days. However, it can vary slightly depending on the species and individual rat.
Litter size Rats have large litters, with an average litter size of 6 to 12 pups. However, litter sizes can vary, and it's not uncommon for a rat to have 15 or more pups in a single litter.
Maternal care Female rats provide maternal care to their offspring. They nurse the pups, keep them warm, and groom them. The mother rat is protective of her young and will defend them against potential threats.
Rapid reproduction Rats are known for their ability to reproduce rapidly. After giving birth, a female rat can quickly become fertile again, often within 24 to 48 hours. This rapid reproductive cycle allows rat populations to grow quickly under favorable conditions.
It's important to note that rats can breed throughout the year, as they are not restricted to specific breeding seasons. This, coupled with their ability to reproduce rapidly, can contribute to the exponential growth of rat populations if not effectively controlled.
To manage rat populations, it is crucial to address rodent infestations promptly, implement effective rodent control measures and take preventive actions such as proper sanitation, sealing entry points, and removing potential food sources. Seeking professional assistance from The Rodent Pros can help ensure comprehensive and efficient rat control.
Signs of Rodents
-Droppings and urine
-Sounds of scratching or chewing in walls and attic
-Dirt marks around holes or along wires or pipes
-Gnawed wires or wood
-Paper or clothes with holes in them
-Leaking water line to dishwasher
Rats are sneaky and will take advantage of any opening to access your home, furthermore, they are more than happy to chew their way in! There are several techniques to reduce the risk of rats entering your home plus methods of removing access points. First, in the garden hiding spots need to be identified because rats prefer not to be observed as they move around. The solution is to cut back or remove high grass or thick vegetation close to the house. Secondly, inspect your home high and low for entry points. Remember that rats are good climbers; so don’t forget to look up. Once you find a hole, it’s time to seal it up. Holes around the exterior of the home can be sealed with surface concrete or additional mortar. If you find holes around internal pipework or in walls there are various methods to use such as cutting a steel plate to insert around a pipe, repairing plasterboard holes, or filling gaps with steel wool as rats can’t chew through it.
Rats have a special place in the history of human infection. The “Black Death” in the 14th Century killed over 25 million people, attributed to fleas born on the fur of rats that were easily transported between countries as stowaways on ships. Rats have an array of ways to transmit diseases and each way promotes a set of health problems. Contamination can come via rodent urine or feces on food or utensils, through bacteria entering cuts or scratches on the skin, this can happen indirectly to pets or humans via fleas, contamination occurs when a person is bitten by a rat, or indirect contamination by eating an intermediate carrier. Diseases spread by rats include Salmonella, Meningitis, Leptospirosis (Weil’s disease), Typhus fever, Favus, Rat-bite fever and Trichinosis. It is imperative that you do not consume food you suspect has been interfered with by a rat as this establishes a direct line of contamination to your body.